
The heterogeneity of ALK mutations in NSCLC
ALK mutations known to confer resistance to TKI therapy
Heterogeneity of mutations is well recognized across ALK+ NSCLC tumor types and is a major challenge for oncologists due to its evolving impact on treatment resistance.1–3
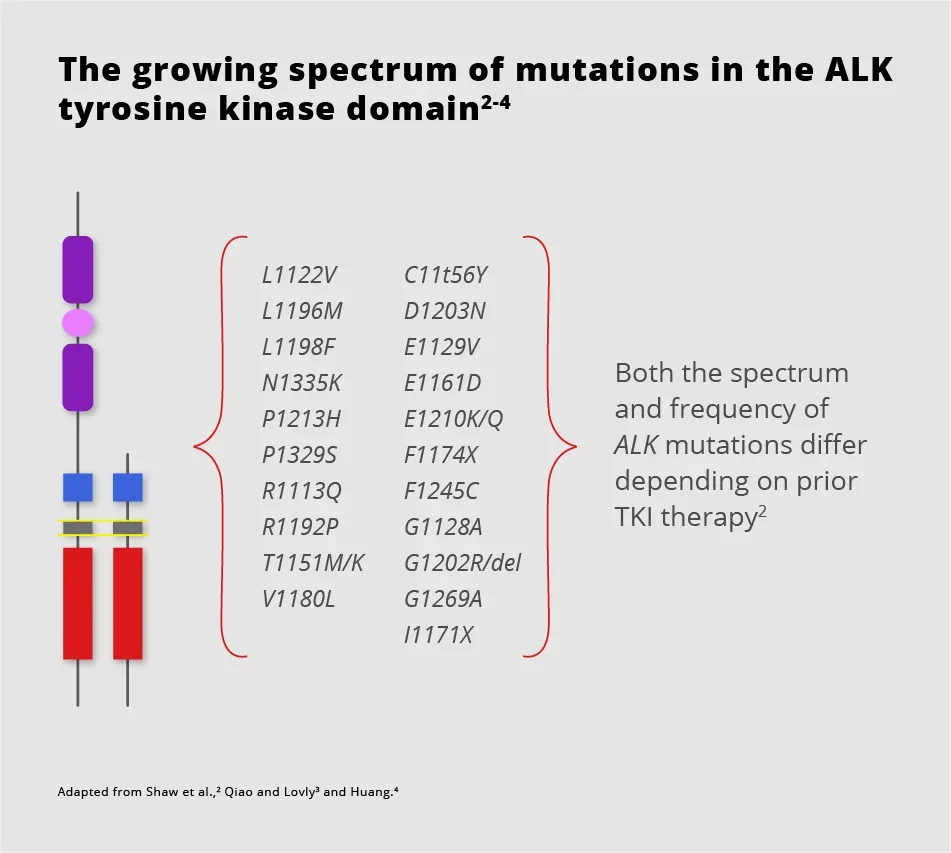
Over 20 different ALK mutations are known to confer resistance to TKI and the number of identified heterogeneous mutations in the ALK tyrosine kinase domain continues to increase.2,3

The heterogeneity of mutations found in patients with acquired resistance to ALK TKI therapy highlights the need for next-generation therapies, designed to overcome secondary resistance.2,3
ALK+ NSCLC remains largely incurable due to the expanding spectrum of oncogenic driver mutations known to confer TKI resistance1-3
LEARN ABOUT ALK+ NSCLC TREATMENT GUIDELINES
ALK(+): anaplastic lymphoma kinase (positive); NSCLC: non-small-cell lung cancer.
1. Rotow J, Bivona TG. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:637–58.
2. Shaw AT, et al. ALK resistance mutations and efficacy of lorlatinib in advanced anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37:1370–9.
3. Qiao H, Lovly M. Cracking the code of resistance across multiple lines of ALK inhibitor therapy in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016;6:1084–6.
4. Huang H. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) receptor tyrosine kinase: a catalytic receptor with many faces. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:3448.