
The scope of resistance mechanisms in ALK+ NSCLC
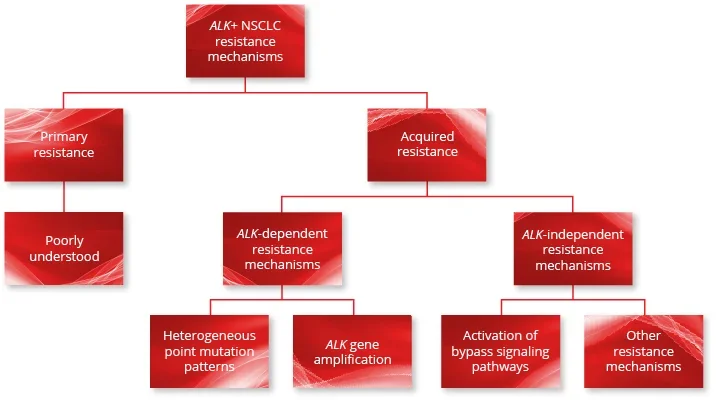
Resistance to ALK TKI therapy can be either primary or acquired1
Primary resistance implies an intrinsic lack of response to treatment.1 Acquired resistance implies disease progression after initial response (partial or complete) to treatment.1
Although primary resistance is poorly understood, acquired resistance can fall broadly under two categories:1
ALK-dependent resistance mechanisms
Secondary mutations in the ALK tyrosine kinase domain
ALK-independent resistance mechanisms
Activation of bypass signaling pathways
Acquired resistance can emerge from a wide spectrum of ALK-dependent or ALK-independent mechanisms of resistance following first-line ALK TKI therapy.1–4
ALK-dependent resistance mechanisms, such as point mutations in the ALK tyrosine kinase domain and ALK gene amplification, are known to alter ALK TKI therapy sensitivity.1,2
ALK-independent resistance mechanisms involve the activation of bypass signaling pathways through genetic alteration and lead to tumor cell survival and proliferation even after ALK inhibition.1
The point mutation patterns observed in patients with ALK+ NSCLC following ALK TKI therapy are highly heterogeneous.2,5

Most patients who respond to first-generation ALK TKI therapy will eventually relapse due to acquired resistance2,4
LEARN ABOUT HETEROGENEOUS MUTATIONS
ALK(+): anaplastic lymphoma kinase (positive); NSCLC: non-small-cell lung cancer; TKI: tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
1. Sharma GG, et al. Tumor resistance against ALK targeted therapy — where it comes from and where it goes. Cancers. 2018;10:62.
2. Katayama R, et al. Therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in lung cancer: a paradigm for precision cancer medicine. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:2227–35.
3. Toyokawa G, Seto T. Updated evidence on the mechanisms of resistance to ALK inhibitors and strategies to overcome such resistance: Clinical and preclinical data. Oncol Res Treat. 2015;38:291–8.
4. Camidge DR, Doebele RC. Treating ALK positive lung cancer: early successes and coming challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9:268–77.
5. Katayama R, et al. Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung cancers. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:120ra17.