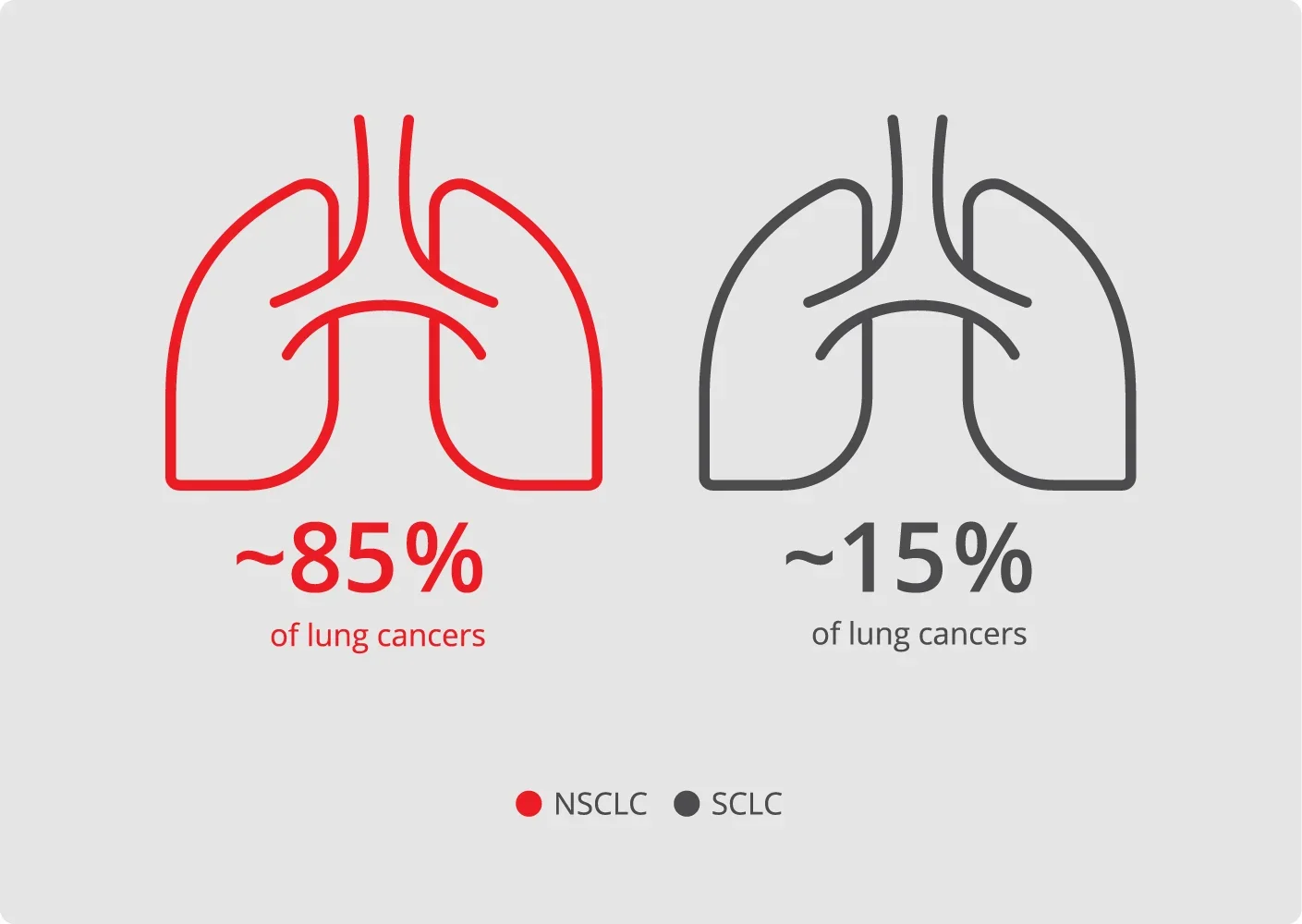

NSCLC is the most common subtype of lung cancer1
Lung cancer is classified into two main histologic subtypes1

NSCLC is further divided into three pathologic subtypes: 2
adenocarcinoma 40%
squamous-cell carcinoma 25–30%
large-cell carcinoma 5–10%
![]()
Over 65% of never-smokers with lung cancer are diagnosed with adenocarcinoma.3
Other less common NSCLC subtypes consist of mixed histology, such as adenosquamous or sarcomatoid carcinomas.4
NSCLC and brain metastases
Up to 35% of newly diagnosed patients may already be impacted by brain metastases5-8
Up to 75% of patients develop brain metastases during the course of their disease6,9,10
NSCLC may also be classified based on molecular subtypes, such as ROS1, RET, MET, BRAF, HER2 and KRAS. The focus of this website is on the molecular subtypes known as ALK and EGFR.2
ALK: anaplastic lymphoma kinase; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; NSCLC: non-small-cell lung cancer; SCLC: small-cell lung cancer.
1. Oser MG, et al. Transformation from non-small-cell lung cancer to small-cell lung cancer: molecular drivers and cells of origin. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:e165–72.
2. Zappa C, Mousa SA. Non-small cell lung cancer: current treatment and future advances. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016;5:288–300.
3. Chapman AM, et al. Lung cancer mutation profile of EGFR, ALK, and KRAS: meta-analysis and comparison of never and ever smokers. Lung Cancer. 2016;102:122–34.
4. European Lung Foundation, European Cancer Patient Coalition, RARECARENet. Rare lung cancers. Breathe (Sheff). 2015;11:323–30.
5. Rangachari D, et al. Brain metastases in patients with EGFR-mutated or ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancers. Lung Cancer. 2015;88:108–11.
6. Descourt R, et al. Brigatinib in patients with ALK-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer pretreated with sequential ALK inhibitors: A multicentric real-world study (BRIGALK study). Lung Cancer. 2019;136:109–14.
7. Johung KL, et al. Extended survival and prognostic factors for patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer and brain metastasis. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:123–9.
8. Guérin, et al. Brain metastases in patients with ALK+ non-small cell lung cancer: clinical symptoms, treatment patterns and economic burden. J Med Econ. 2015;18:312–22.
9. Huber RM, et al. Brigatinib in Crizotinib-Refractory ALKþ NSCLC: 2-Year Follow-up on Systemic and Intracranial Outcomes in the Phase 2 ALTA Trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2020;15:404–15.
10. Solomon BJ, et al. Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: results from a global phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:1654–67.